This article will discuss:
- The method of determining the limiting oxygen concentration in dust clouds in a closed vessel
- The method of determining the limiting oxygen concentration in dust clouds under predetermined conditions of pressure and temperature
- The procedure to be followed
The experts at Dinnissen Process Technology are available to answer all your questions:
Get in touch with Juul Jenneskens 077 467 3555
Determine limit oxygen concentration in dust clouds in a closed vessel
Normally, a vessel capable of withstanding the explosion pressure of 1 m3 is used to determine the limit oxygen concentration. That barrel is used to determine three things:
- the maximum explosion pressure,
- the maximum speed of explosion pressure rise, also called the Kst value,
- the lowest explosion limit of dust clouds.
The vessel is usually spherical or cylinder-shaped and must be designed to withstand at least 20 bar overpressure. In addition, this equipment must be equipped with electrical or mechanical disconnections as well as possible. To ensure that openings in the vessel, such as the inlet and outlet, are properly closed before starting the (test) procedure. In addition, the equipment must also be designed in such a way that residual pressure in the vessel can be vented.
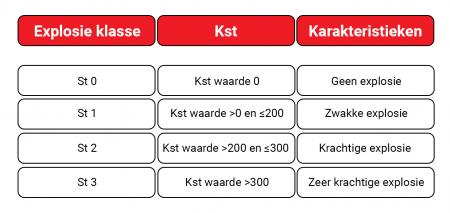
Oxygen concentration values
Determine oxygen limit concentration in dust clouds under predetermined conditions
The dust dispersal system works as follows. The dust to be spread at the top of the system is placed in a large dust container with a volume of 5.4 dm3, the aspect ratio being 3: 1. This dust container has an outlet through which the dust leaves the container. This outlet is closed by a fast acting valve that is activated by a jet cap. The seal is in the form of a small ring. That ring is destroyed by firing a jet cap and the valve opens due to the pressure in the dust container. The valve is designed to open in less than 10 milliseconds and is connected to the side of the blast vessel. To disperse the dust, a semicircular spray pipe is mounted on the inside of the blast vessel, similar to the shape of the wall. This spray pipe has 13 holes each with a diameter of 6 millimeters.
The ignition source in the dust distribution system consists of two electrically activated pyrotechnic igniters, each with an ignition energy of 5 kJ. These are placed in the opposite direction in the center of the blast barrel. The detonators are ignited in less than 10 milliseconds by electrical fuse heads.
The pressure measuring system contains at least two pressure sensors and recording equipment. It has an accuracy of about 0.1 bar and a time resolution of 1 millisecond. The system used to measure the oxygen concentration has an accuracy of approximately 0.1% (v/v).

Oxygen concentration conditions for dust explosion
In the next step the vessel is filled with a mix of an inert gas and air of the desired oxygen content. That oxygen content must be checked by an oxygen analyzer
The Oxygen Limit Concentration Procedure
The oxygen limiting concentration (LOC) is created by initially increasing the ratio of inert gas to air step by step and varying it with the dust concentration. This will reduce the oxygen concentration to a level where no more explosions can occur. The oxygen limit concentration does not only depend on the type of substance, but also on the type of inert gas. In order for the oxygen concentration in the vessel to be the correct value at the time of ignition, the following approach is required.
The vessel is filled with a mix of an inert gas and air of the desired oxygen content. That oxygen content must be checked by an oxygen analyzer. For consecutive measurements with the same nominal oxygen concentration, the oxygen concentration should be within approximately 0.3% V / V of the nominal value.
Then the required amount of dust is placed in the dust container. This should not be more than three-quarters of the way through the dust container, so that good pressure remains possible. If this is not possible, two dispersion systems with 5.4 dm3 dust bins must be used in parallel. This tank can be pressurized with a mix of air and inert gas, with the same nominal oxygen concentration as in the vessel. as with only air. In both cases up to an overpressure of 20 bar.
The time between the start of the dust emission and the activation of the ignition source, also called the ignition delay, is 0.6 ± 0.01. In addition, the pressure is recorded as a function of time. From the pressure-time curve the explosion pressure (Pex) and the speed of the rise of the explosion pressure (dp/dt) can then be determined.
The maximum permissible deviations when it comes to the dp/dtmax are as follows:
De maximale toelaatbare afwijkingen als het gaat om de dp/dtmax zijn als volgt
| dp/dtmax bar · s-1 | Relative deviation |
| < 50 | ± 30 |
| >50 tot 100 | ± 20 |
| >100 tot 200 | ± 12 |
| >200 | ± 10 |
Ultimately, the ignition of the dust, the explosion, has taken place when the measured overpressure in relation to the initial pressure (p1) equals 0.3 bar.
Finally, after each test, the explosion vessel should be cleaned and both the test equipment and procedure should be checked and checked every 12 months or after major repairs.

Name: Juul Jenneskens
Advisor
Please feel free to contact me if you have any questions about this subject. My team of colleagues and I are ready to answer!
Get in touch with Juul Jenneskens 077 467 3555 [email protected]
Do you prefer to request a consultation directly?
